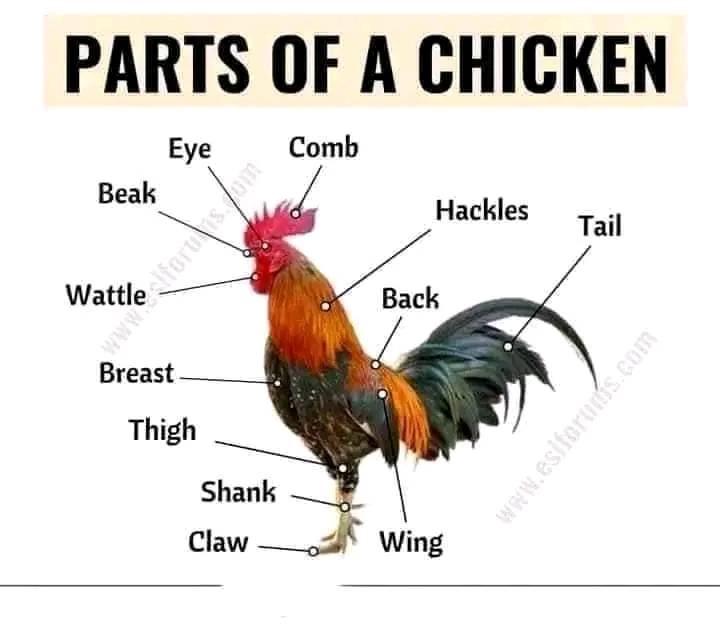
Here’s a description and uses of each part of a chicken:
1. Eye
- Description: The eye is a vital sensory organ.
- Uses: Allows the chicken to see and detect predators, navigate its environment, and find food.
2. Beak
- Description: The beak is hard and pointed.
- Uses: Used for pecking at food, drinking water, and grooming feathers.
3. Comb
- Description: The fleshy crest on top of the head.
- Uses: Helps regulate body temperature and can indicate health and maturity, particularly in males.
4. Wattle
- Description: The fleshy skin hanging under the beak.
- Uses: Helps with temperature regulation and is also a secondary sexual characteristic.
5. Hackles
- Description: The feathers on the neck.
- Uses: Can be raised when the chicken is excited or threatened, serving as a display mechanism.
6. Tail
- Description: The feathers at the rear.
- Uses: Helps with balance and communication; also plays a role in mating displays.
7. Back
- Description: The upper body of the chicken.
- Uses: Supports the body structure and is where muscles for movement are anchored.
8. Breast
- Description: The front, meaty part of the chicken.
- Uses: A significant source of meat in culinary uses, especially in poultry dishes.
9. Thigh
- Description: The upper part of the leg.
- Uses: Provides meat that is flavorful and often used in various recipes.
10. Shank
- Description: The part of the leg between the knee and the foot.
- Uses: Supports the chicken while walking and is often included in culinary dishes.
11. Claw
- Description: The feet of the chicken, ending in sharp nails.
- Uses: Used for scratching the ground to find food and for defense.
12. Wing
Uses: While domestic chickens are not strong fliers, wings are used for balance and can help in short bursts of flight. They are also a source of meat.
Description: The appendage used for flight.

Here’s a description and uses of each part of a chicken based on the new image:
1. Comb
- Description: The fleshy crest on the top of the chicken’s head.
- Uses: Regulates body temperature and signifies health and maturity, especially in males.
2. Eye
- Description: The sensory organ that enables sight.
- Uses: Helps the chicken detect predators, navigate its surroundings, and find food.
3. Tail
- Description: The feathers at the rear of the chicken.
- Uses: Provides balance and aids in communication, especially during mating displays.
4. Beak
- Description: The hard, pointed mouth of the chicken.
- Uses: Used for pecking at food, drinking, and grooming feathers.
5. Wattle
- Description: The fleshy skin that hangs under the beak.
- Uses: Assists in temperature regulation and serves as a secondary sexual characteristic.
6. Breast
- Description: The meaty front part of the chicken.
- Uses: A primary source of meat in poultry dishes, known for its tenderness.
7. Thigh
- Description: The upper part of the chicken’s leg.
- Uses: Provides flavorful meat, commonly used in various recipes.
8. Shank
- Description: The part of the leg between the knee and the foot.
- Uses: Supports the chicken while walking and is often included in culinary dishes.
9. Wing
- Description: The appendage used for limited flight.
- Uses: While not strong fliers, wings help with balance and are also a source of meat.
10. Toe
- Description: The digits of the chicken’s foot.
- Uses: Used for scratching the ground to find food and for gripping surfaces.
11. Back
Uses: Supports body structure and is where muscles for movement are attached.
Description: The upper part of the chicken’s body.

Here’s a description and uses of each part of a duck based on the new image:
1. Crown
- Description: The top part of the duck’s head.
- Uses: Often reflects the breed and can be a visual marker for identification.
2. Nape
- Description: The back of the neck.
- Uses: Provides flexibility and movement for the head; also contributes to visual appearance.
3. Neck
- Description: The elongated part connecting the head to the body.
- Uses: Allows the duck to reach food, especially in water, and aids in communication.
4. Bill
- Description: The flat, broad mouth.
- Uses: Used for foraging, feeding, and grooming; plays a role in filter feeding.
5. Nostrils
- Description: The openings on the bill.
- Uses: Allow the duck to breathe and detect scents, crucial for foraging.
6. Bean
- Description: The small, fleshy part at the tip of the bill.
- Uses: Helps in tactile sensing and feeding.
7. Mantle
- Description: The feathers covering the back and sides.
- Uses: Provides insulation and protection; contributes to the duck’s overall appearance.
8. Wing
- Description: The appendage used for flight.
- Uses: Enables flying short distances and aids in balance; also provides meat.
9. Back
- Description: The upper part of the duck’s body.
- Uses: Supports body structure and muscle attachment for movement.
10. Tail
- Description: The feathers at the rear.
- Uses: Aids in balance and communication, especially during mating displays.
11. Undertail Coverts
- Description: The feathers underneath the tail.
- Uses: Provide insulation and can aid in mating displays.
12. Shank
- Description: The part of the leg between the knee and the foot.
- Uses: Supports the duck while walking and swimming.
13. Foot
- Description: The webbed extremities used for swimming.
- Uses: Provides propulsion in water and helps in walking on land.
14. Belly
Uses: Contains the digestive organs and is a source of meat.
Description: The underside of the duck.

Here’s a description and uses of each part of a bird based on the new image:
1. Crown
- Description: The top part of the bird’s head.
- Uses: Often reflects species characteristics and can be used for identification.
2. Nape
- Description: The back of the neck.
- Uses: Provides flexibility for head movement and contributes to the bird’s appearance.
3. Forehead
- Description: The area between the eyes and the beak.
- Uses: Aids in visual identification and can display species-specific markings.
4. Eye
- Description: The organ for vision.
- Uses: Essential for navigating the environment, spotting food, and avoiding predators.
5. Upper Beak
- Description: The top part of the beak.
- Uses: Used for feeding, grooming, and manipulating objects.
6. Lower Beak
- Description: The bottom part of the beak.
- Uses: Complements the upper beak for feeding and other functions.
7. Chin
- Description: The area below the lower beak.
- Uses: Helps in feeding and can play a role in visual displays.
8. Feather
- Description: The structures covering the body.
- Uses: Provide insulation, aid in flight, and play a role in camouflage and display.
9. Back
- Description: The upper part of the bird’s body.
- Uses: Supports muscle attachment and provides structural integrity.
10. Wing
- Description: The appendage used for flight.
- Uses: Enables flying and provides balance; also serves as a source of meat.
11. Tail
- Description: The feathers at the rear.
- Uses: Aids in balance during flight and can be used for communication.
12. Thigh
- Description: The upper part of the leg.
- Uses: Supports movement and provides muscle for flight.
13. Leg
- Description: The limb supporting the body.
- Uses: Provides mobility on land and stability during perching.
14. Foot
- Description: The part of the leg ending in toes.
- Uses: Used for grasping, perching, and walking; also aids in foraging.
15. Undertail Coverts
- Description: The feathers underneath the tail.
- Uses: Provide insulation and can enhance visual displays during courtship.
16. Upperpart Coverts
Uses: Protect underlying feathers and contribute to the bird’s overall appearance.
Description: The feathers covering the upper body.
Discover more from ELIMU ASSISTANT
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.